Results
73 results found

Tourist development construction building work, Drymades Beach, Dhermi, Albanian Riviera, Albania, Europe
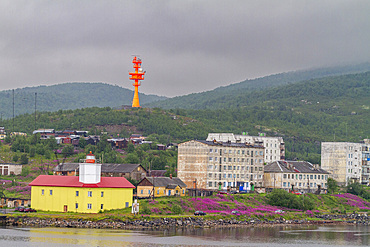
A view of the industrial and militarized Russian seaport city of Murmansk on the northern shore of the Kola Peninsula, Murmansk Oblast, Russia, Arctic, Europe

A view of the industrial and militarized Russian seaport city of Murmansk on the northern shore of the Kola Peninsula, Murmansk Oblast, Russia, Arctic, Europe

The Iceberg apartment building in the new quarter Aarhus East constructed by the expansion of the harbour area, Aarhus, Jutland Peninsula, Denmark, Europe

Red Crane Truck on Sunny Wharf with Coastal Mountains and Calm Sea in South Bay Harbour, Kaikoura Peninsula, New Zealand

Coastal road beside blue sea with mountain views and work in progress sign at Kaikura Peninsula, South Island, New Zealand

Views of the abandoned whale processing station at Whalers Bay on Deception Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, Polar Regions

View of Port of Kavala, Dimos Kavalas, Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, Gulf of Thasos, Gulf of Kavala, Thracian Sea, Greece, Europe

Bridge connecting Sur Township to Al Ayjah village, port-city, capital of Ash Sharqiyah Region, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Panorama of Tangier port at sunrise with industrial cranes and mountains in the background, Tangier, Morocco

Corinth Canal connecting the Gulf of Corinth in the Ionian Sea with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea, Greece

Corinth Canal connecting the Gulf of Corinth in the Ionian Sea with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea, Greece

Metallic bridge crossing the Corinth Canal connecting the Gulf of Corinth in the Ionian Sea with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea, Greece

Corinth Canal connecting the Gulf of Corinth in the Ionian Sea with the Saronic Gulf in the Aegean Sea, Greece

Drone aerial view of Kriaritsi project area with abandoned roads in the south of Greece, Sithonia, Chalkidiki, Greece

Drone aerial view of Kriaritsi project area with abandoned roads in the south of Greece, Sithonia, Chalkidiki, Greece

Drone aerial view of Kriaritsi project area with abandoned roads in the south of Greece, Sithonia, Chalkidiki, Greece

Drone aerial view of Kriaritsi project area with abandoned roads in the south of Greece, Sithonia, Chalkidiki, Greece

Drone aerial view of Kriaritsi project area with abandoned roads in the south of Greece, Sithonia, Chalkidiki, Greece

Views of the abandoned whaling station in Stromness Bay on South Georgia in the Southern Ocean, Polar Regions

A view of the industrial and militarized Russian seaport city of Murmansk on the northern shore of the Kola Peninsula, Murmansk Oblast, Russia, Arctic, Europe

View of the fishing town of Westmanna on the west side of Streymoy Island in the Faroe Islands, Denmark

Nan'ao bridge, 9.3 km long, connecting mainland Shantou City to resort island of Nan'ao Island, Shantou City, Guangdong Province, China

A collapsed coastal road near Skipsea on Yorkshires East Coast, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all playing their part.

A collapsed coastal road at between Skipsea and Ulrome on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

A collapsed coastal road at between Skipsea and Ulrome on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

A collapsed coastal road at Easingotn on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

A collapsed coastal road at near Aldbrough on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

Concrete sea defences at Beach Bank Caravan Park in Ulrome near Skipsea on Yorkshires East Coast, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This section of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all playing their part.

A collapsed coastal road at between Skipsea and Ulrome on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

A Second world War lookout post leaning alarmingly and about to tumble over the edge of the cliff near Aldbrough on Yorkshires East Coast, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This section of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all playing their part.

A collapsed coastal road at Barmston on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

Waves crashing off Parton near Whitehaven during the January 2014 period of storm surge, high tides and storm force winds. The coastline took a battering, damaging the harbour wall and eroding a large section of coastal cliff.

Whitehaven harbour during the January 2014 period of storm surge, high tides and storm force winds. The coastline took a battering, damaging the harbour wall and eroding a large section of coastal cliff.

Whitehaven harbour being completely overwhelmed by huge waves during the January 2014 period of storm surge, high tides and storm force winds. The coastline took a battering, damaging the harbour wall and eroding a large section of coastal cliff.

Whitehaven harbour during the January 2014 period of storm surge, high tides and storm force winds. The coastline took a battering, damaging the harbour wall and eroding a large section of coastal cliff.

Medieval city palaces, Palazzi, built on rock at the steep cliffs, fishing boats in the port, Marina del Vescovado, Porto di Tropea, Vibo Valentia, Calabria, Tyrrhenian Sea, South Italy, Italy, Europe

Medieval city palaces, Palazzi, built on rock at the steep cliffs, boats in the port, Marina del Vescovado, Porto di Tropea, Vibo Valentia, Calabria, Tyrrhenian Sea, South Italy, Italy, Europe

Medieval city palaces, Palazzi, built on rock at the steep cliffs, boats in the port, Marina del Vescovado, Porto di Tropea, Vibo Valentia, Calabria, Tyrrhenian Sea, South Italy, Italy, Europe

Medieval city palaces, Palazzi, built on rock at the steep cliffs, fishing boats in the port, Marina del Vescovado, Porto di Tropea, Vibo Valentia, Calabria, Tyrrhenian Sea, South Italy, Italy, Europe



























































