Results
48 results found

Sunset at the Salt pan polygons, Badwater Basin, 282ft below sea level and the lowest place in North America, Death Valley National Park, California, United States of America, North America

Rising to 260 feet above sea level, Makatea is a raised coral atoll with fresh water, Tuamotus, French Polynesia, South Pacific, Pacific

Rising to 260 feet above sea level, Makatea is a raised coral atoll with fresh water, Tuamotus, French Polynesia, South Pacific, Pacific

Lulworth Cove, a perfect horseshoe-shaped bay, Jurassic Coast, UNESCO World Heritage Site, Dorset, England, United Kingdom, Europe

Rising to 260 feet above sea level, Makatea is a raised coral atoll with fresh water, Tuamotus, French Polynesia, South Pacific, Pacific

View from the top of Sfornioi nord mount 2410 meters above sea level, Dolomites, eastern Alps, Veneto, Italy, Europe

El Tatio Geysers, at 4300m above sea level El Tatio is the world's highest geyser field, the area is ringed by volcanoes and fed by 64 geysers, Atacama Desert, Norte Grande, Chile, South America

El Tatio Geysers, at 4300m above sea level El Tatio is the world's highest geyser field, the area is ringed by volcanoes and fed by 64 geysers, Atacama Desert, Norte Grande, Chile, South America

Snorkelers swim above a blue hole on Palau's barrier reef. This hole formed when sea level was much lower than it is today.

View of tidewater glacier deep inside Neko Harbor on the western side of the Antarctic Peninsula, Southern Ocean, Polar Regions

El Tatio Geysers, 4300m above sea level, El Tatio is the world's highest geyser field, the area is ringed by volcanoes and fed by 64 geysers, Atacama Desert, Norte Grande, Chile, South America

Salt pan polygons at Badwater Basin, 282ft below sea level and the lowest place in North America, Death Valley National Park, California, United States of America, North America

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Blue iceberg arch in snowy weather, from sea level, Waterboat Point, Paradise Bay, Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctica, Polar Regions

Blue icebergs in snowy weather, from sea level, Waterboat Point, Paradise Bay, Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctica, Polar Regions

Estancia Colome, vineyards located in the high Calchaqui valley at 2300 meters above sea level, Salta Province, Argentina, South America

Bodega Colome, a winery located in high Calchaqui valley at 2300 meters above sea level, Salta Province, Argentina, South America

The intertidal zone of the Quantock Coast, West Somerset, contains an abundance of geology and wildlife. It is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) and is of international geological importance.

The intertidal zone of the Quantock Coast, West Somerset, contains an abundance of geology and wildlife. It is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) and is of international geological importance.
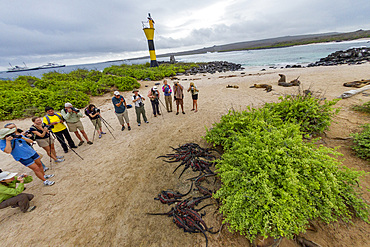
The endemic Galapagos marine iguana (Amblyrhynchus cristatus) on Espanola Island in the Galapagos Islands, UNESCO World Heritage Site, Ecuador, South America

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Breakfast at Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Blue icebergs in snowy weather, from sea level, Waterboat Point, Paradise Bay, Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctica, Polar Regions

Lava lizard (Microlophus spp) in the Galapagos Islands Archipelago, UNESCO World Heritage Site, Ecuador, South America

Bodega Colome, a winery located in high Calchaqui valley at 2300 meters above sea level, Salta Province, Argentina, South America

Buddhist prayer flags around the gate to Sela mountain pass at 13700 feet above sea level, Arunachal Pradesh, India, Asia

El Tatio Geysers, at 4300m above sea level El Tatio is the world's highest geyser field, the area is ringed by volcanoes and fed by 64 geysers, Atacama Desert, Norte Grande, Chile, South America

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Alila Jabal Akhdar hotel, nestled 2000 metres above sea level, surrounded by Al Hajar Mountains, Sultanate of Oman, Arabian Peninsula

Adult Subantarctic Skua (Catharacta antarctica lonnbergi) on tussac at Salisbury Plain on South Georgia Island, Polar Regions

A commercial whale watching boat being launched at the beach at low tide in Puerto Pyramides, Golfo Nuevo, Argentina, South America

Salt pan polygons at Badwater Basin, 282ft below sea level and the lowest place in North America, Death Valley National Park, California, United States of America, North America

Sunset at the Salt pan polygons, Badwater Basin, 282ft below sea level and the lowest place in North America, Death Valley National Park, California, United States of America, North America

A permanent springfed pool near the salt pans at Badwater Basin, 282ft below sea level and the lowest place in North America, Death Valley National Park, California, United States of America, North America

Sunset at Mount Everest (Mount Sagarmatha), Zhumulangma Peak, the world's highest mountain, 8,848 metres above sea level, Tibet, China, Asia

Salt pan polygons at Badwater Basin, 282ft below sea level and the lowest place in North America, Death Valley National Park, California, United States of America, North America

Salt pan polygons at Badwater Basin, 282ft below sea level and the lowest place in North America, Death Valley National Park, California, United States of America, North America

A WWF project to supply electricity to a remote island in the Sunderbans, a low lying area of the Ganges Delta in Eastern India, that is very vulnerable to sea level rise. Prior to this project the subsistence farmers had no access to electricity. The project involves charging large batteries from solar panels. Each villager collects a battery to run household lighting, and returns to the recharging station once a week to recharge their battery. This shot shows women carrying the heavy batteries (20Kg) from the charging station.

A WWF project to supply electricity to a remote island in the Sunderbans, a low lying area of the Ganges Delta in Eastern India, that is very vulnerable to sea level rise. Prior to this project the subsistence farmers had no access to electricity. The project involves charging large batteries from solar panels. Each villager collects a battery to run household lighting, and returns to the recharging station once a week to recharge their battery. This shot shows women carrying the heavy batteries (20Kg) from the charging station.

A collapsed coastal road near Skipsea on Yorkshires East Coast, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all playing their part.

A collapsed coastal road at between Skipsea and Ulrome on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

A collapsed coastal road at between Skipsea and Ulrome on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

A collapsed coastal road at Easingotn on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

A collapsed coastal road at near Aldbrough on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

Concrete sea defences at Beach Bank Caravan Park in Ulrome near Skipsea on Yorkshires East Coast, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This section of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all playing their part.

A collapsed coastal road at between Skipsea and Ulrome on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

A Second world War lookout post leaning alarmingly and about to tumble over the edge of the cliff near Aldbrough on Yorkshires East Coast, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This section of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all playing their part.

A collapsed coastal road at Barmston on Yorkshires East Coast, near Skipsea, UK. The coast is composed of soft boulder clays, very vulnerable to coastal erosion. This sectiion of coast has been eroding since Roman times, with many villages having disappeared into the sea, and is the fastest eroding coast in Europe. Climate change is speeding up the erosion, with sea level rise, increased stormy weather and increased heavy rainfall events, all palying their part.

Cow dung belonging to subsistence farmers in the Sunderbans, a low lying area of the Ganges Delta in Eastern India, that is very vulnerable to sea level rise. The cow dung is used as biofuel in traditional clay ovens.

A BP chemical plant at salt End on Humberside which produces Acetic Acid and a gas fired power station It is vulnerable to coastal flooding, and although sea defences were constructed some years ago, climate change driven sea level rise and increased stromy weather, leaves it vulnerable to inundation.

Villagers in a remote subsistence farming village on an island in the Sunderbans, the Ganges Delta in Eastern India that is very vulnerable to sea level rise, gather in the rice crop after drying.

A woman drying her rice crop in the Sunderbans, Ganges, Delta, India, the area is very low lying and vulnerable to sea level rise.

Villagers in a remote subsistence farming village on an island in the Sunderbans, the Ganges Delta in Eastern India that is very vulnerable to sea level rise, gather in the rice crop after drying.

A woman subsistence farmer cooking on a traditional clay oven, using rice stalks as biofuel in the Sunderbans, Ganges, Delta, India. the area is very low lying and vulnerable to sea level rise. All parts of the rice crop are used, and the villagers life is very self sufficient, with a tiny carbon footprint.
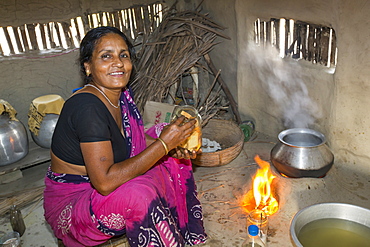
A villager woman in a remote subsistence farming village on an island in the Sunderbans, the Ganges Delta in Eastern India that is very vulnerable to sea level rise. She is cooking on a traditional clay oven, fuelled by biofuel (rice stalks), low carbon cooking.

The Thames barrier on the River Thames in London. It was constructed to protect the capital city from storm surge flooding. Recent predictions show it will probably be redundant in around twenty years due to increased stormy weather and sea level rise driven by climate change.

The Thames barrier on the River Thames in London. It was constructed to protect the capital city from storm surge flooding. Recent predictions show it will probably be redundant in around twenty years due to increased stormy weather and sea level rise driven by climate change.

The Thames barrier on the River Thames in London. It was constructed to protect the capital city from storm surge flooding. Recent predictions show it will probably be redundant in around twenty years due to increased stormy weather and sea level rise driven by climate change.

The Remains of the Godwin battery on the beach at Kilnsea at the head of Spurn point on Yorkshires East Coast, UK. Initially constructed during the First World War, the Godwin Battery was added to during the Second World War. It comprised of gun emplacements, search light, barracks, officers’ mess, and a hospital. This section of coastline is the fastest eroding coastline in Europe. The soft boulder clay cliffs are easily eroded and have been eroding since Roman Times, but recently the climate change impacts of increased stormy weather, increased heavy rainfall events and sea level rise have accelerated the rate of erosion. The average rate of attrition is 1.5metres per year, last year it was 5 metres.

The Remains of the Godwin battery on the beach at Kilnsea at the head of Spurn point on Yorkshires East Coast, UK. Initially constructed during the First World War, the Godwin Battery was added to during the Second World War. It comprised of gun emplacements, search light, barracks, officers’ mess, and a hospital. This section of coastline is the fastest eroding coastline in Europe. The soft boulder clay cliffs are easily eroded and have been eroding since Roman Times, but recently the climate change impacts of increased stormy weather, increased heavy rainfall events and sea level rise have accelerated the rate of erosion. The average rate of attrition is 1.5metres per year, last year it was 5 metres.

Villagers in a remote subsistence farming village on an island in the Sunderbans, the Ganges Delta in Eastern India that is very vulnerable to sea level rise, gather in the rice crop after drying.

Cow dung belonging to subsistence farmers in the Sunderbans, a low lying area of the Ganges Delta in Eastern India, that is very vulnerable to sea level rise. The cow dung is used as biofuel in traditional clay ovens.

An RV on the road near Badwater which is the lowest point in the USA being 282 feet below sea level in Death Valley. Death Valley is the lowest, hottest, driest place in the USA, with an average annual rainfall of around 2 inches, some years it does not receive any rain at all.

Mount Terevaka, a young volcano, the highest point on the island, 511 m above sea level, Easter Island, Chile, South America

Boats carrying people and goods in the Sunderbans, a low lying area of the Ganges Delta in Eastern India, that is very vulnerable to sea level rise.

A sign at 100 feet below sea level in Death Valley which is the lowest, hottest, driest place in the USA, with an average annual rainfall of around 2 inches, some years it does not receive any rain at all.

Highly built up beach front areas, just north of Atlantic City that are very vulnerable to sea level rise, USA.

Boats carrying people and goods in the Sunderbans, a low lying area of the Ganges Delta in Eastern India, that is very vulnerable to sea level rise.

Boats carrying people and goods in the Sunderbans, a low lying area of the Ganges Delta in Eastern India, that is very vulnerable to sea level rise.

Mount Terevaka, a young volcano, the highest point on the island, 511 m above sea level, Easter Island, Chile, South America

Girls face an uncertain future as their island home is threatened by global warming induced sea level rise, Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu, Pacific

Tuvaluans watch as the high tide inundates their island home due to global warming induced sea level rise, Funafuti, Tuvalu, Pacific

Pulaka that has been killed off by salt water incursion caused by global warming induced sea level rise, Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu, Pacific

Trees knocked down by undercutting coastal erosion caused by global warming induced sea level rise on Tepuka island off Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu, Pacific

A teenage girl sits in the floodwater caused by sea water incursion due to global warming induced sea level rise that threatens the future of these low lying islands, Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu, Pacific

Boy wading through the floodwater caused by sea water incursion due to global warming induced sea level rise that threatens the future of these low lying islands, Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu, Pacific

Sea water incursion onto Funafuti Atoll the main island, as global warming induced sea level rise threatens to flood these low lying islands, Funafuti, Tuvalu, Pacific

Boy playing in the floodwater caused by sea water incursion due to global warming induced sea level rise that threatens the future of these low lying islands, Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu, Pacific

Trees knocked down by undercutting coastal erosion caused by global warming induced sea level rise on Tepuka island off Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu, Pacific

Sea water incursion onto Funafuti Atoll the main island, as global warming induced sea level rise threatens to flood these low lying islands, Funafuti, Tuvalu, Pacific

The Breach at Alkborough created in the sea defences to allow sea water to flood agricultural land and create a wetland for wildlife, Humber Estuary, Humberside, England, United Kingdom, Europe

Surveying the floodwater caused by sea water incursion due to global warming induced sea level rise that threatens the future of these low lying islands, Funafuti Atoll, Tuvalu, Pacific

Sea water incursion onto Funafuti Atoll the main island, as global warming induced sea level rise threatens to flood these low lying islands, Funafuti, Tuvalu, Pacific








