Results
12 results found

Desalinisation plant at the solar energy scientific research centre, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Heliostats reflect sunrays to receiver tower, solar energy scientific research centre, AORA Tulip System, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Heliostats reflecting sun rays, solar energy scientific research centre, AORA Tulip System, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

A traditional mud hut home with a thatched roof and a solar panel on the top of it, Tanzania, East Africa, Africa

Parabolic discs at the solar energy scientific research centre, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Solar panel array in field in countryside providing domestic energy near village of Rogil, Algarve district, Portugal, Europe

Heliostats at the solar energy scientific research centre, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Curved concave reflector panels desalinisation plant at the solar energy scientific research centre, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Array of solar panels on a bright sunny day, Sierra Alhamilla, near Nijar, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Large heliostat EuroDish solar energy scientific research centre, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Heliostats and central receiver CESA-1 Tower at solar energy scientific research centre, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Curved concave reflector panels desalinisation plant at the solar energy scientific research centre, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

Faro de Cíes lighthouse, Isla del Faro island, Cies Islands, Atlantic islands National Park, Galicia, Spain, Europe

Parabolic discs at the solar energy scientific research centre, Tabernas, Almeria, Andalusia, Spain, Europe

A light-filled elementary classroom. A white ceiling reflects light from the windows above. Traditional building methods and materials, such as the poplar and willow ceilings are combined with modern solar and passive solar technology. Druk Padma Karpo Institute. Shey, Ladakh, India

A light-filled elementary classroom. A white ceiling reflects light from the windows above. Traditional building methods and materials, such as the poplar and willow ceilings are combined with modern solar and passive solar technology. Druk Padma Karpo Institute. Shey, Ladakh, India

The Kamal factory in Bangalore, Karnataka, India that manufactures solar thermal panels for heating water.

Asia's largest solar popwer station, the Gujarat Solar Park, in Gujarat, India. It has an installed capacity of 1000 MW

The Kamal factory in Bangalore, Karnataka, India that manufactures solar thermal panels for heating water.

Asia's largest solar popwer station, the Gujarat Solar Park, in Gujarat, India. It has an installed capacity of 1000 MW

Asia's largest solar popwer station, the Gujarat Solar Park, in Gujarat, India. It has an installed capacity of 1000 MW

Asia's largest solar power station, the Gujarat Solar Park, in Gujarat, India. It has an installed capacity of 1000 MW

Women constructing solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. The use of the cookers, vastly reduces the amount of fire wood women have to go out and collect from the forest.

Women welding joints during the construction of solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Solar cookers save women having to walk to the froest to cut down wood for cooking, thus saving the forests, and a daily chore for woman.

Women on a solar workshop, learning how to make solar lanters at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Many of the women are iliterate or semi literate. They are trained from countries all over the world, so that they can take their skills back and cascade the learning.

Women on a solar workshop, learning how to make solar lanters at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Many of the women are iliterate or semi literate. They are trained from countries all over the world, so that they can take their skills back and cascade the learning.

Solar panelsproviding electricity at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people.

Women building solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people.
Women on a solar workshop, learning how to make solar lanters at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Many of the women are iliterate or semi literate. They are trained from countries all over the world, so that they can take their skills back and cascade the learning.

Women on a solar workshop, learning how to make solar lanters at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Many of the women are iliterate or semi literate. They are trained from countries all over the world, so that they can take their skills back and cascade the learning.

Solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. The use of the cookers, vastly reduces the amount of fire wood women have to go out and collect from the forest.

Women welding joints during the construction of solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Solar cookers save women having to walk to the froest to cut down wood for cooking, thus saving the forests, and a daily chore for woman.

Women on a solar workshop, learning how to make solar lanters at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Many of the women are iliterate or semi literate. They are trained from countries all over the world, so that they can take their skills back and cascade the learning.

Women constructing solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. The use of the cookers, vastly reduces the amount of fire wood women have to go out and collect from the forest.

Women welding joints during the construction of solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Solar cookers save women having to walk to the froest to cut down wood for cooking, thus saving the forests, and a daily chore for woman.

Women constructing solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people.

Women constructing solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India, demonstrate how hot the device is, by holding a sheet of newspaper which instantly sets on fire in the 300 degree Celcius heat. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. The use of the cookers, vastly reduces the amount of fire wood women have to go out and collect from the forest.

Women constructing solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people.

Women on a solar workshop, learning how to make solar lanters at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Many of the women are iliterate or semi literate. They are trained from countries all over the world, so that they can take their skills back and cascade the learning.
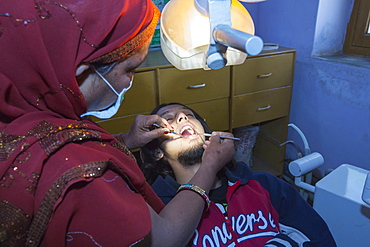
A Barefoot Dentist, who is trained to perform basic dentistry at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people.

Women on a solar workshop, learning how to make solar lanters at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. Many of the women are iliterate or semi literate. They are trained from countries all over the world, so that they can take their skills back and cascade the learning.

Women constructing solar cookers at the Barefoot College in Tilonia, Rajasthan, India. The Barefoot College is a worldwide charity, founded by Bunker Roy, its aims are, education, drinking water, electrification through solar power, skill development, health, women empowerment and the upliftment of rural people. The use of the cookers, vastly reduces the amount of fire wood women have to go out and collect from the forest.

Asia's largest solar popwer station, the Gujarat Solar Park, in Gujarat, India. It has an installed capacity of 1000 MW. Here workers wash dust off the panels to increase their efficiency.

The Muni Seva Ashram in Goraj, near Vadodara, India, is a tranquil haven of humanitarian care. The Ashram is hugely sustainable, next year it will be completely carbon neutral. Its first solar panels were installed in 1984, long before climate change was on anyones agenda. Their energy is provided from solar panels, and wood grown on the estate. Waste food and animal manure is turned inot biogas to run the estates cars and also used for cooking. Solar cookers are also used, and the air conditioning for the hospital is solar run. 70 % of the food used is grown on the estate. They provide an orphanage, schools for all ages, vocational training, care for the elderly, a specialist cancer hospital withstate of the art machinary, and even have a solar crematorium. This shot shows a cook preparing chapatis on a biofuel stove.

The Muni Seva Ashram in Goraj, near Vadodara, India, is a tranquil haven of humanitarian care. The Ashram is hugely sustainable, next year it will be completely carbon neutral. Its first solar panels were installed in 1984, long before climate change was on anyones agenda. Their energy is provided from solar panels, and wood grown on the estate. Waste food and animal manure is turned inot biogas to run the estates cars and also used for cooking. Solar cookers are also used, and the air conditioning for the hospital is solar run. 70 % of the food used is grown on the estate. They provide an orphanage, schools for all ages, vocational training, care for the elderly, a specialist cancer hospital withstate of the art machinary, and even have a solar crematorium. This shot shows solar panels that focus the suns rays on heat exchangers to boil oil, which is then sent down to the kitchens below to heat the cookers.

The Muni Seva Ashram in Goraj, near Vadodara, India, is a tranquil haven of humanitarian care. The Ashram is hugely sustainable, next year it will be completely carbon neutral. Its first solar panels were installed in 1984, long before climate change was on anyones agenda. Their energy is provided from solar panels, and wood grown on the estate. Waste food and animal manure is turned inot biogas to run the estates cars and also used for cooking. Solar cookers are also used, and the air conditioning for the hospital is solar run. 70 % of the food used is grown on the estate. They provide an orphanage, schools for all ages, vocational training, care for the elderly, a specialist cancer hospital withstate of the art machinary, and even have a solar crematorium. This shot shows the solar air conditioning for the Ashram's hospital.
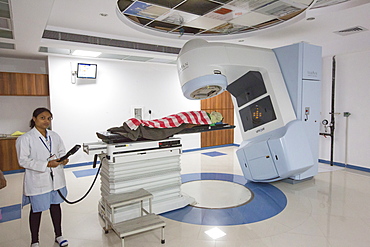
The Muni Seva Ashram in Goraj, near Vadodara, India, is a tranquil haven of humanitarian care. The Ashram is hugely sustainable, next year it will be completely carbon neutral. Its first solar panels were installed in 1984, long before climate change was on anyones agenda. Their energy is provided from solar panels, and wood grown on the estate. Waste food and animal manure is turned inot biogas to run the estates cars and also used for cooking. Solar cookers are also used, and the air conditioning for the hospital is solar run. 70 % of the food used is grown on the estate. They provide an orphanage, schools for all ages, vocational training, care for the elderly, a specialist cancer hospital withstate of the art machinary, and even have a solar crematorium. This shot shows a Varian nuclear proton therapy machine in the specialist cancer hospital.

The Muni Seva Ashram in Goraj, near Vadodara, India, is a tranquil haven of humanitarian care. The Ashram is hugely sustainable, next year it will be completely carbon neutral. Its first solar panels were installed in 1984, long before climate change was on anyones agenda. Their energy is provided from solar panels, and wood grown on the estate. Waste food and animal manure is turned inot biogas to run the estates cars and also used for cooking. Solar cookers are also used, and the air conditioning for the hospital is solar run. 70 % of the food used is grown on the estate. They provide an orphanage, schools for all ages, vocational training, care for the elderly, a specialist cancer hospital withstate of the art machinary, and even have a solar crematorium. This shot shows a woman planting trees for onward growth in the Ashrams forests.

The Muni Seva Ashram in Goraj, near Vadodara, India, is a tranquil haven of humanitarian care. The Ashram is hugely sustainable, next year it will be completely carbon neutral. Its first solar panels were installed in 1984, long before climate change was on anyones agenda. Their energy is provided from solar panels, and wood grown on the estate. Waste food and animal manure is turned inot biogas to run the estates cars and also used for cooking. Solar cookers are also used, and the air conditioning for the hospital is solar run. 70 % of the food used is grown on the estate. They provide an orphanage, schools for all ages, vocational training, care for the elderly, a specialist cancer hospital withstate of the art machinary, and even have a solar crematorium. This shot shows the girls school.

Electric cars being recharged at the Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

Workers washing the heliostats to maximise reflective power at the Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

Electric cars being recharged at the Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

Workers washing the heliostats to maximise reflective power at the Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

Workers washing the heliostats to maximise reflective power at the Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

Electric cars being recharged at the Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

The 354 megawatts SEGS plant at Kramer Junction is the second largest solar thermal power plant in the world, mojave Desert, California, USA.

Pylons carrying solar electric from the Copper Mountain Solar 3 project, is a 250-megawatt solar power plant that produces enough energy to power 80, 000 homes, in Nevada, USA.

The 354 megawatts SEGS plant at Kramer Junction is the second largest solar thermal power plant in the world, mojave Desert, California, USA.

The Kamal factory in Bangalore, Karnataka, India that manufactures solar thermal panels for heating water.

A light-filled elementary classroom. A white ceiling reflects light from the windows above. Traditional building methods and materials, such as the poplar and willow ceilings are combined with modern solar and passive solar technology. Druk Padma Karpo Institute. Shey, Ladakh, India

The Ivanpah Solar Thermal Power Plant in California''s Mojave Desert is currently the largest solar thermal plant in the world. It generates 392 megawatts (MW) and deploys 173,500 heliostats that reflect the suns rays onto three solar towers. It covers 4,000 acres of desert.

Tracking solar voltaic panels outside the University of Central Lancashire, Preston, Lancashire, England, United Kingdom, Europe

Tracking solar voltaic panels outside the University of Central Lancashire, Preston, Lancashire, England, United Kingdom, Europe

Tracking solar voltaic panels outside the University of Central Lancashire, Preston, Lancashire, England, United Kingdom, Europe
























